Is Tpu Screen Protector Shock Resistant?
Table of Contents
Summary
Tempered glass, a type of safety glass that undergoes a specialized heat treatment, is lauded for its strength, impact resistance, and ability to shatter into small, less dangerous pieces upon breaking, making it an ideal choice for mobile phone screens. Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) screen protectors, on the other hand, offer exceptional flexibility, impact resistance, and self-healing properties, catering to a wide range of consumer needs and preferences. Tempered glass screen protectors have a rich history dating back centuries with the development of “Prince Rupert’s Drops” and have since evolved through various patented methods. Today, these protectors are known for their robust scratch resistance, improved display quality, and easy maintenance. They also feature oleophobic and antimicrobial coatings that enhance optical clarity and hygiene, though they may crack from edge damage and are often thicker than other alternatives. The production of tempered glass involves heating normal glass to high temperatures and rapidly cooling it to create a durable, tension-balanced tructure.
TPU screen protectors, produced through an extrusion process, are characterized by their durability, flexibility, and transparency. These protectors conform well to curved screens and maintain excellent touch sensitivity and display clarity. Despite their many advantages, including easy installation and removal, TPU protectors can discolor over time and are less hard compared to tempered glass, which might not appeal to users desiring a glass-like feel. Both types of screen protectors are part of a market that is heavily influenced by
advances in screen technology, consumer preferences, and sustainability initiatives. Manufacturers strive to balance high performance with environmental responsibility by reducing harmful substances and embracing recycling practices. The market trends also reflect a growing consumer demand for screen protectors that offer additional features, such as anti-slip grips and wireless charging compatibility,
without compromising on protection and clarity. In summary, the choice between tempered glass and TPU screen protectors often
depends on individual priorities and use cases. While tempered glass offers superior protection and a premium feel, TPU provides flexibility and self-healing capabilities. Both play crucial roles in enhancing the longevity and usability of mobile devices in an increasingly technology-driven world.
History
Though the underlying mechanism was not known at the time, the effects of tempering glass have been recognized for centuries. Around 1660, Prince Rupert of the Rhine introduced what are now known as “Prince Rupert’s Drops” to King Charles II. These are teardrop-shaped bits of glass produced by allowing molten glass to fall into water, cooling it rapidly. These drops can withstand a hammer blow on the bulbous end without breaking but will disintegrate explosively if the tail end is slightly damaged. Francois Barthelemy Alfred Royer de la Bastie of Paris, France, is credited with first developing a method of tempering glass by quenching nearly molten glass in a heated bath of oil or grease in 1874. This method was patented in England on August 12, 1874 (patent number 2783). As a result, tempered glass is sometimes known as Bastie glass. In 1877, the German inventor Friedrich Siemens developed a different process known as compressed glass or Siemens glass. This method produced tempered glass stronger than the Bastie process by pressing the glass in cool molds. The first patent on an entire process to make tempered glass was held by chemist Rudolph A. Seiden, born in 1900 in Austria and emigrated to the United States in 1935. These advancements laid the groundwork for the modern methods of producing tempered glass, which involve heating the glass to a high temperature and then rapidly cooling it to increase its strength and shatter resistance.
Materials and Manufacturing
Reducing Harmful Substances
Glass manufacturing, while integral to the tech ecosystem, has not been without its environmental implications. The use of hazardous substances in the production process has long been a point of concern. In response, a transformative shift is underway – one that’s focused on reducing the employment of harmful materials. This initiative extends beyond glass itself, weaving its way into the broader ethos of
electronics manufacturing. Initiatives such as RoHS compliance – an endeavor that restricts the use of hazardous substances – underscore the industry’s commitment to responsible practices. By embracing these regulations, manufacturers aim to deliver cutting-edge technology while minimizing the potential harm to both consumers and the environment. Moreover, the manufacturing process isn’t merely about functionality; it extends to environmental responsibility too. Forward-thinking manufacturers are actively embracing sustainable practices and recyclable materials to minimize their ecological impact.
Tempered Glass Manufacturing
The strength of tempered glass is a direct result of its manufacturing process. Normal annealed glass is heated in a special furnace to temperatures exceeding 600° Celsius. This softens its entire structure. Its surface is then suddenly and quickly cooled, usually with the help of special air blasters. As a result, the inside of the glass solidifies faster than the outside, creating extreme tension between the two parts. These tensional forces toughen the glass, giving it exceptional strength and making it up to five times stronger than annealed glass of comparable size and thickness. Tempered glass can stand up to impact, scratch, and high heat levels, making it an ideal choice for mobile phone screens. The base material is primarily composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2) with small amounts of other minerals, which offers good clarity and light transmission but can be brittle and prone to shattering into sharp shards upon impact. The tempering process transforms this regular glass into a much stronger, safer, and more versatile product suitable for safety-focused applications.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) Film Manufacturing
Understanding the nuances between TPU film, polyurethane film, and other thermoplastics is pivotal for industry professionals making material selection decisions. TPU is a type of polyurethane and shares many properties with polyurethane films. However, TPU is precisely engineered to be thermoplastic, meaning it can be melted, shaped, and re-solidified multiple times without significantly degrading its properties. Traditional polyurethane typically undergoes a one-time thermosetting process, making it less amenable to recycling and reshaping[7]. The production of high-quality TPU film involves the extrusion process—a method where TPU pellets are heated until they reach a melt state. This molten TPU is then forced through a flat-die extrusion process, which shapes the TPU into a thin film while maintaining uniform thickness across its surface. Key to this process is the precise control of temperature, pressure, and speed, which dictates the film’s final properties such as tensile strength, elasticity, and clarity.
Environmental Considerations
The environmental impact of TPU film production involves both resource consumption and emissions. The production process is energy-intensive, requiring significant amounts of electricity and raw materials derived from fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. However, TPU film’s recyclability presents an opportunity to mitigate these environmental impacts. Recycling TPU film reduces the demand for virgin materials and lowers the carbon footprint associated with its production.
Characteristics of Mobile Phone Tempered Glass
Tempered glass is a specialized type of safety glass that undergoes a heat treatment to improve its durability and resistance to impact and shattering. This makes it an ideal choice for protecting mobile phone screens.
Safety
One of the key benefits of tempered glass is its enhanced safety features. If tempered glass breaks, it shatters into small, rounded pieces that are less likely to cause injury compared to the sharp shards produced by regular glass. This makes it a safer option for mobile phone screens, which are prone to accidental drops and impacts.
Scratch Resistance
Tempered glass has a hard surface that is resistant to scratches, making it particularly suitable for touch screens and other digital displays that are subject to frequent touches and contacts. This ensures that the screen remains clear and free from unsightly marks over time.
Improved Display Quality
The smooth surface of tempered glass helps to improve the visual clarity and color accuracy of a display. This enhances the overall user experience, making images and videos appear more vibrant and clear.
Easy to Clean
Tempered glass is easy to clean and less likely to harbor bacteria, which is especially important for applications where hygiene is a priority, such as medical displays or food preparation surfaces. This makes it a practical choice for mobile phone screens that are frequently touched.
Heat Resistance
Tempered glass can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for use in electronic devices that generate heat. This characteristic ensures that the glass does not warp or degrade under thermal stress, maintaining its integrity and protective qualities.
Impact Resistance
Tempered glass can absorb the impact and protect the original screen from damage when the device is subjected to physical stress, such as being dropped or rubbed against other objects. This impact resistance is one of the primary reasons for its popularity as a screen protector.
Drawbacks
Despite its many advantages, tempered glass does have some drawbacks. It tends to crack from one end to the other if the edge of the glass is damaged due to the stress placed on it during the tempering process. Additionally, the thickness of tempered glass may not be suitable for users who prefer a thinner and lighter device.
Hardness Rating
Many tempered glass screen protectors advertise a “9H” hardness rating for extra impact and scratch protection. However, this rating does not accurately reflect the material’s true hardness on the Mohs scale, where even the strongest tempered glass would be unlikely to surpass a 6-7 rating.
Oleophobic and Antimicrobial Coatings
An oleophobic coating, designed to reduce smudging and blotting from oils on fingers, is common for most touchscreen devices, including those with tempered glass protectors. This coating enhances optical clarity but wears off over time. Similarly, an antimicrobial coating can reduce the growth of surface bacteria and mold, contributing to the cleanliness and hygiene of the device
Installation Types
There are different installation methods for tempered glass screen protectors. Dry installation involves carefully aligning the protector to the display and using a soft cloth to remove air bubbles. Wet installation requires applying a liquid adhesive before placing the protector on the display.
Touch Sensitivity and Visual Clarity
The responsiveness of touch screens is attributed to the precision engineering of tempered glass, which registers even the gentlest taps and swipes accurately.
Characteristics of Mobile Phone TPU Screen Protector
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) phone screen protectors are a popular choice among consumers seeking robust protection for their mobile devices. These protectors offer a blend of flexibility, durability, and clarity, making them highly effective in safeguarding screens from various forms of damage.
Durability and Flexibility
TPU screen protectors are known for their exceptional durability and flexibility. Made from a thin, flexible material, these protectors can absorb impacts and resist bending without cracking. This elasticity allows the TPU protectors to stretch and return to their original shape, maintaining their integrity even under stress. Moreover, TPU’s ability to conform to curved screens ensures comprehensive coverage and protection for modern smartphones with edge-to-edge displays.
Impact and Scratch Resistance
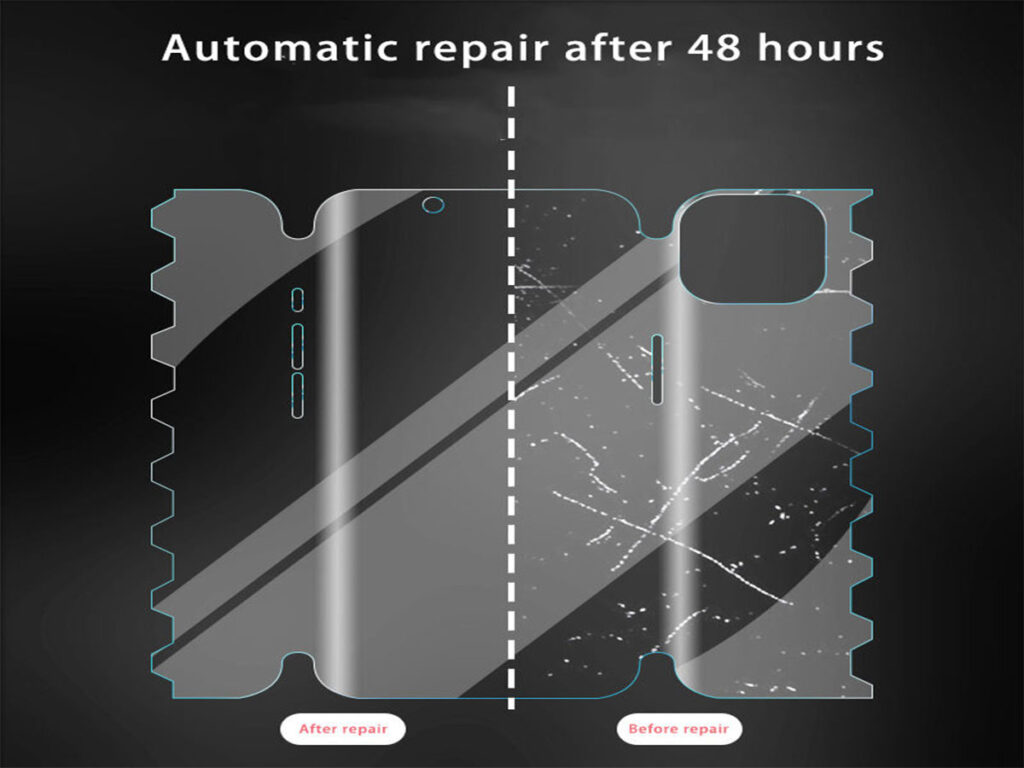
One of the standout features of TPU protectors is their impact resistance. They are designed to absorb shocks and prevent scratches and cracks, which is particularly beneficial for users who frequently carry their phones in pockets or bags. TPU film also possesses self-healing properties, enabling it to automatically repair minor scratches and maintain a smooth surface.
Transparency and Touch Sensitivity
TPU screen protectors are highly transparent, allowing users to enjoy their phone’s ull display without distortion. This high level of clarity ensures that the screen remains vivid and clear. Additionally, TPU protectors maintain touchscreen sensitivity, ensuring that the user experience is not compromised.
Ease of Installation and Removal
Another advantage of TPU screen protectors is their ease of installation and removal. These protectors can be applied without bubbles and removed without leaving residue, making them a convenient and user-friendly option for phone screen protection.
Limitations
Despite their many benefits, TPU screen protectors have some limitations. They can be prone to discoloration from prolonged exposure to sunlight and may accumulate oil residue from fingertips. Furthermore, while TPU protectors offer a good level of protection, they do not provide the same hardness as tempered glass protectors, which may be preferred by some users for a more glass-like feel.
Comparisons
Tempered and Gorilla Glass differ significantly in terms of properties, damage resistance, and applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed decisions about their use. Pricing varies based on manufacturer agreements and bulk purchasing deals. Generally, Gorilla Glass is priced higher due to its established reputation, while newer entrants like Panda Glass may offer competitive pricing to attract cost-conscious manufacturers. Huawei’s Kunlun Glass represents a notable advancement in smartphone display technology, promising enhanced durability and clarity. The ongoing advancements in smartphone and cellular technologies often make long-term investment in highly durable screens less practical for average consumers 17. Sapphire Glass is mainly used in smaller smartphone components like camera lenses and fingerprint sensors due to its high cost, though some luxury smartphones feature full Sapphire Glass screens. The Kyocera Brigadier was the first production smartphone to have a sapphire screen, introduced in 2014 on the Verizon Wireless network. Comparatively, each glass type offers distinct advantages:
Gorilla Glass: Known for its excellent durability and scratch resistance, it remains a popular choice among manufacturers.
Panda Glass: Offers similar durability and scratch resistance, often at a lower price point.
Kunlun Glass: Developed by Huawei, it emphasizes strength and toughness, competing directly with other high-durability glasses.
Longing Glass: Introduced by Xiaomi, it is known for its scratch resistance and durability, offering unique performance characteristics. Screen protectors also vary significantly in materials and performance. Traditional PET films provide essential scratch protection but lack the durability and impact resistance of newer polyurethane (PU) films. PU films offer superior elasticity,enhancing protection against drops and extending the protector’s lifespan by withstanding various environmental challenges. Plastic screen protectors are lightweight and effective for scratch protection, but they fall short in clarity, feel, and impact resistance compared to tempered glass. These are ideal for users primarily concerned with scratch protection and seeking a lightweight solution.
Testing Methods
Hardness Testing
Hardness testing for mobile phone screen protectors, particularly tempered glass, typically involves using pencils with varying degrees of scratching power. This process begins with the softest pencil, marked as 6B, and proceeds to harder pencils until one is found that can scratch the surface. The Mohs hardness rating of a material is determined by the hardest pencil that manages to scratch it. For tempered glass screen protectors, this is usually the 9H pencil, and this rating indicates the scratch resistance of the screen protector. However, it is important to note that this hardness rating does not measure impact resistance, flexibility, or other types of durability.
Drop Test
The drop test is another common method used to assess the quality of a screen protector. This test involves placing a drop of water on the flat surface of the screen protector and observing the shape of the water drop. If the drop spreads out with an angle of less than 110 degrees, the screen protector is considered to have poor steel technology. A more rounded water drop indicates better quality.
Wear Resistance Testing
Wear resistance is tested using a #0000 steel velvet to rub the screen protector 3,000 times. This test is designed to simulate prolonged use and ensure that the screen protector can withstand friction over time without significant wear and tear.
Fracture Testing
Fracture testing evaluates the elasticity of tempered glass by subjecting it to an external force. The glass is bent and then returned to its original state once the force is removed. This test verifies the product’s stability and consistency, reducing the risk of breakage. Additionally, a breaking test is performed where the glass is bent around a half circle. If it breaks but remains in two whole segments, it passes the test.
Anti-Fingerprint Testing
To ensure that screen protectors can resist fingerprint smudges, anti-fingerprint coatings are applied. There are two main methods for this: spray coating and vacuum coating. Spray coating is less durable and uniform compared to vacuum coating, which provides a more lasting anti-fingerprint effect.
Quality Control
Throughout the manufacturing process, rigorous quality control measures are implemented. Raw materials are inspected for durability, clarity, and resistance to scratches and impacts. Regular checks are conducted to monitor the accuracy of cutting and shaping, ensuring that each screen protector fits its designated device model. Final inspections involve thorough testing for defects or imperfections, ensuring that only high-quality products reach consumers.
Popular Brands and Products
When selecting a screen protector for your mobile phone, considering reputable brands can guide you toward a high-quality product. Well-known companies such as Spigen, Whitestone Dome, and AmFilm are celebrated for their tempered glass protectors, receiving consistently positive reviews and high Mohs hardness ratings for their durability and scratch resistance. For those who prefer TPU screen protectors, ArmorSuit is a standout brand, offering TPU films that are renowned for their flexibility and ability to extend closer to the edges of the screen compared to standard options, which is beneficial for users who opt not to use a phone case. OtterBox and Zagg also produce premium PET hybrid models that can be nearly indistinguishable from glass, providing a robust alternative to traditional tempered glass protectors. Among recent flagship smartphones, glass and ceramic designs have become prominent, with models such as the LG G7, HTC U12 Plus, and Xiaomi Mi 8 showcasing this trend. More affordable options, like the HONOR 10 and HONOR 8 from HUAWEI’s HONOR series, also feature sophisticated glass designs, indicating that quality screen protection is not limited to high-end devices. It’s important to ensure proper installation for these protectors. High-quality products often come with tools like brackets for precise alignment and may use LOCA (Liquid Optically Clear Adhesive) for enhanced clarity and strong adhesion. Misalignment, even by a small margin, can cause issues such as peeling or interference with phone cases. In terms of distribution, screen protectors are widely available through multiple channels including online marketplaces, electronics stores, and specialized accessory retailers. Many manufacturers also sell directly to consumers via their websites, fostering closer customer relationships and offering personalized support. Environmentally conscious buyers might appreciate brands that embrace sustainable practices, such as using eco-friendly packaging materials and exploring carbon-neutral shipping options, reflecting a commitment to reducing environmental impact.

Market Trends
The market for mobile phone tempered glass and TPU screen protectors is characterized by rapid innovation and shifting consumer preferences. The ongoing advancements in screen technologies have led to a significant evolution in the design and functionality of these protective accessories. Among the prominent trends, several key themes stand out.
Consumer Preferences
The choice between tempered glass and TPU screen protectors often depends on individual priorities. While plastic screen protectors offer a minimalist look that preserves the device’s aesthetic, tempered glass protectors provide superior protection against scratches, impacts, and cracks. Consumers who prioritize device aesthetics might lean towards plastic protectors, whereas those seeking robust protection for high-end devices typically opt for tempered glass solutions.
Advanced Screen Technologies
The relentless pursuit of innovation in mobile phone screens has given rise to groundbreaking advancements, including foldable and flexible displays, and scratch-resistant surfaces. These technologies not only enhance the user experience but also drive the demand for more sophisticated protective solutions. Manufacturers like Corning, with their Gorilla Glass, have established a reputation for durability, albeit at a higher price point, while newer players like Panda Glass offer competitive pricing to attract cost-sensitive manufacturers.
Sustainability Initiatives
In response to growing environmental concerns, the mobile phone accessory industry is increasingly embracing sustainable practices. This includes reducing the use of hazardous substances in glass manufacturing and complying with regulations such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances). Additionally, screen protector manufacturers are adopting eco-conscious initiatives, such as sustainable packaging and carbon-neutral shipping options, to reduce their environmental impact.
Retail Distribution Channels
Screen protectors are made available through various retail channels, including online marketplaces, electronics stores, and specialized accessory retailers. The rise of e-commerce has also facilitated direct-to-consumer sales, allowing manufacturers to gather customer feedback and offer personalized support. This direct approach helps build stronger relationships with consumers and better meet their
needs.
Additional Features and Design
TPU screen protectors and phone cases come in a variety of designs, including clear, translucent, or patterned options, allowing consumers to select styles that complement their smartphones while providing the desired level of transparency or visual appeal[27]. Additional features such as anti-slip grips, wireless charging compatibility, and integrated kickstands are also becoming important considerations
for consumers when choosing protective accessories. The market for mobile phone screen protectors continues to evolve, driven by
technological innovations and an increasing emphasis on sustainability and consumer-centric designs. As manufacturers adapt to these trends, the future of mobile phone protection looks promising, balancing advanced technology with responsible practices.
Environmental Impact
The production and disposal of materials used in mobile phone screen protectors have significant environmental implications. One of the primary materials, tempered glass, has an advantage over plastics due to its recyclability and use of bio-available materials such as sand and limestone. This results in less raw material consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to plastic. Additionally,
glass is non-toxic and does not pose harm to human health, further bolstering its environmental credentials.Efforts to reduce harmful substances in the production process are also critical. In glass manufacturing, the adherence to regulations like RoHS compliance highlights the industry’s shift towards minimizing the use of hazardous materials. This initiative is part of a broader commitment to responsible electronics manufacturing, ensuring that technological advancements do not come at the expense of environmental health. The recycling of glass from discarded electronic devices contributes to reducing the environmental burden of new glass production and promotes a circular economy. On the other hand, the production of Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) films, often used in mobile phone screen protectors, involves considerable resource consumption and emissions. The process is energy-intensive, requiring significant amounts of electricity and fossil fuel-derived raw materials, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. However, TPU’s recyclability offers an avenue to mitigate these impacts. Recycling TPU films can lower the demand for virgin materials and reduce the carbon footprint of production, though the overall environmental benefits are heavily dependent on the efficiency and availability of recycling facilities. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting sustainable practices and recyclable materials to minimize their ecological impac. This is evident in the comprehensive preparation of production lines, where advanced equipment and careful material selection ensure efficient and environmentally responsible manufacturing processes. Moreover, integrating additives in thermoplastic production enhances performance while reducing waste and energy use, leading to more competitive and environmentally friendly products. By embracing both recycling and the reduction of harmful substances, the mobile phone screen protector industry is making strides towards aligning technology with environmental consciousness. Each step in salvaging materials and improving production processes is a move towards a more sustainable and responsible tech ecosystem.
Comments

Anti-Glare Matte Screen Protector Film
Reduce glare and fingerprints with our Anti-Glare Matte Screen Protector Film. Enjoy clear visibility in bright conditions, smudge-free screen.

Tempered Glass vs. Hydrogel Screen Protector
Choosing between tempered glass and hydrogel screen protectors depends on your specific needs and preferences.

Matte and Clear Self-Healing EPU
Matte and Clear EPU Film: The ultimate choice in self-healing screen protection. Find the perfect finish for your phone.

How Much Does a Phone Repair Cost?
understanding phone repair costs and options is essential for making informed decisions about your device’s care.

How to Remove a Tempered Glass Screen Protector: A Step-by-Step Guide
Are you struggling with a cracked or bubbled tempered glass screen protector? Don’t worry! This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of safely removing your old screen protector and preparing your device for a fresh start. Whether you’re dealing with a smartphone, tablet, or any other gadget, we’ve got you covered. Read on to discover expert tips, common pitfalls to avoid, and everything you need to know about removing and replacing your tempered glass screen protector.
Tags
Find All knowledge and trends from our blog, get the wholesale price and best quality from our factory.
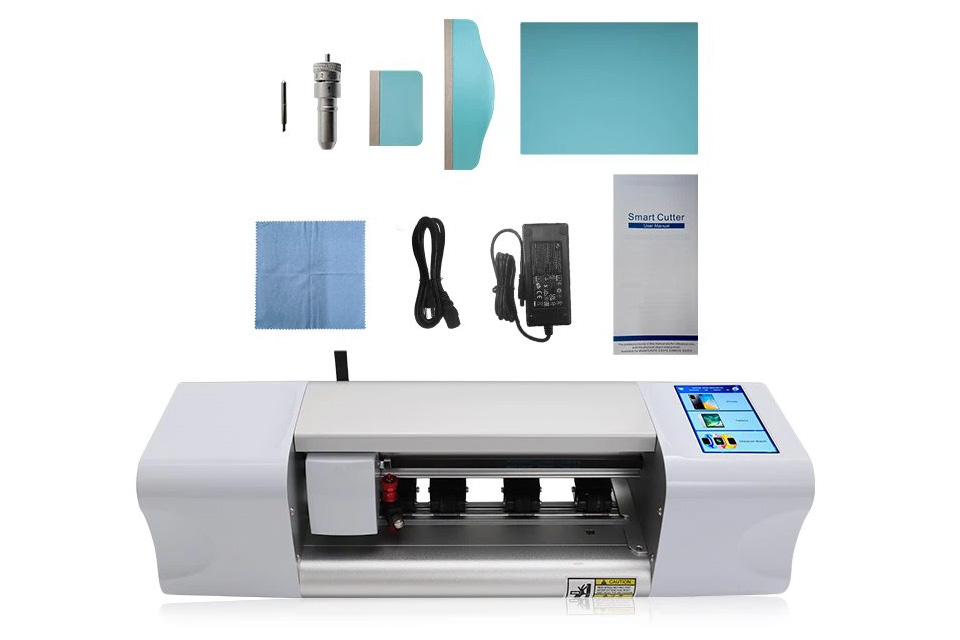

What Film Cutting Machine and Its Application
Film cutting machines have played a crucial role in the evolution of filmmaking and various industrial processes by enabling precise cutting and splicing of film materials.
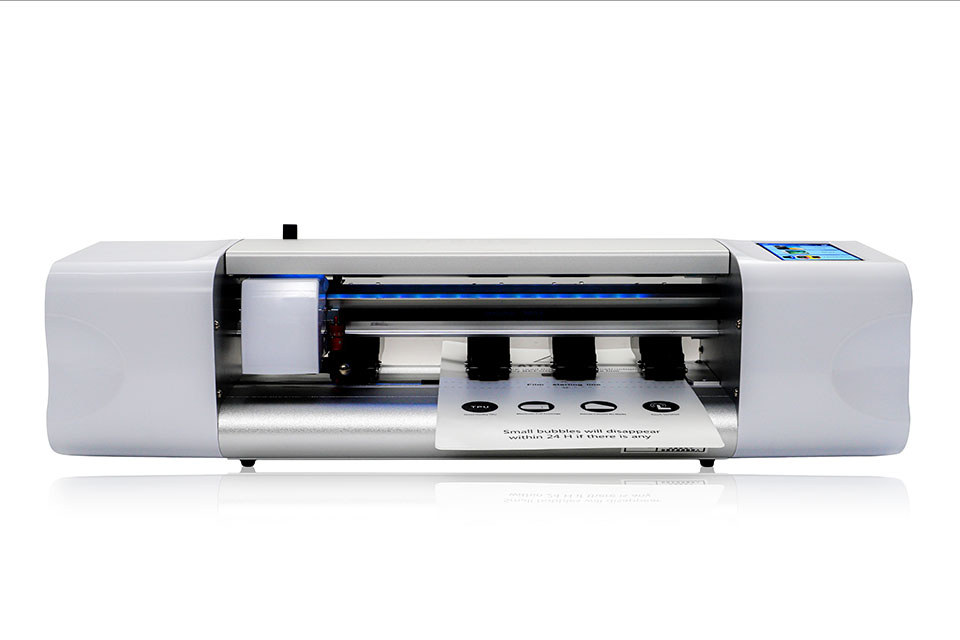

What Is a Screen Protector Cutting Machine?
A screen protector cutting machine is a specialized device designed to produce custom-fit screen protectors for various electronic devices, including smartphones, tablets, smartwatches, laptops, and monitors.
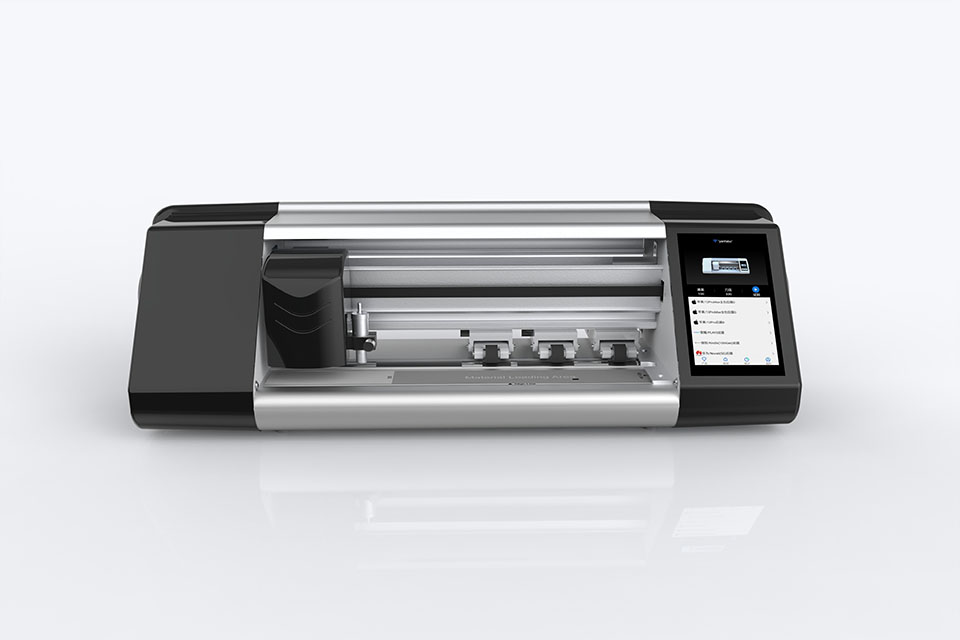

How Mobile Phone Screen Protector Cutting Machine Work?
A mobile phone screen protector cutting machine is a sophisticated device designed
to produce customized screen protectors for various digital devices with high preci
sion and efficiency.
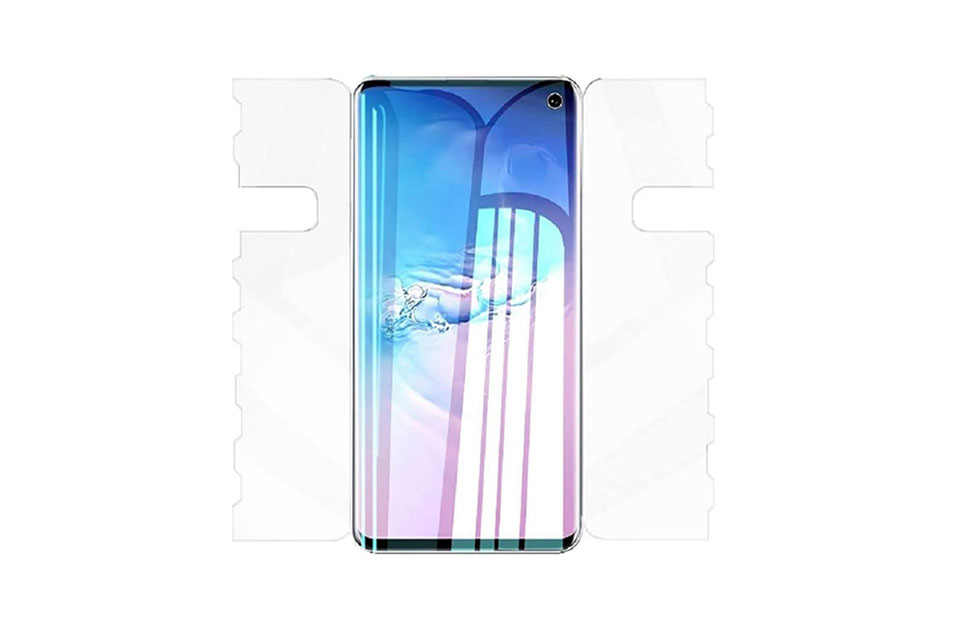

Characteristics of Mobile Phone Tempered Glass and Mobile Phone TPU Screen Protector
Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) screen protectors are flexible, durable, and
self-healing plastic films designed to protect electronic device screens from
scratches, impacts, and other potential damages.

Revolutionize Device Protection with Screen Guard Cutting Machine
Whether you possess a smartphone, tablet, or smartwatch, this versatile machine accommodates a vast array of devices. It seamlessly adapts to the dimensions of your gadget, offering a custom fit that generic protectors can’t match.

Screen Protector Lifetime Warranty
A screen protector lifetime warranty is a guarantee provided by manufacturers that
promises to repair or replace a screen protector for the lifetime of the product, under specific terms and conditions.






