Innovations in Flexible Hydrogel Film Technology
Table of Contents
Extract
Summary
Innovations in flexible hydrogel film technology represent a significant advancement in materials science, combining the principles of polymer chemistry with diverse applications across healthcare, electronics, and environmental sustainability. Hydrogels are three-dimensional polymer networks capable of absorbing significant amounts of water, which makes them uniquely suited for a range of applications, from medical devices to soft robotics. The evolution of hydrogel technology has been marked by the development of smart hydrogels that respond to environmental stimuli, as well as the integration of advanced manufacturing techniques like 3D printing, which enables the production of complex geometries and customized solutions for individual needs.
The notable applications of flexible hydrogel films in tissue engineering highlight their capacity to mimic the extracellular matrix of biological tissues, facilitating cell growth and drug delivery. This has led to breakthroughs in regenerative medicine, such as the creation of patient-specific implants and biocompatible scaffolds. In addition to medical applications, hydrogels are increasingly employed in soft robotics due to their flexibility and ability to change shape in response to external stimuli, thus mimicking biological movements. Furthermore, environmental applications include their use in agriculture and smart packaging, where their moisture retention properties are leveraged to enhance plant growth and monitor food freshness. Despite their promise, the field faces significant challenges, including high production costs, property anisotropy, and sensitivity to surface conditions, which may hinder their widespread adoption. Addressing these limitations is critical for advancing the practical application of hydrogel technology. Ongoing research into biodegradable and sustainable options is also vital, as it aims to mitigate environmental concerns associated with traditional polymers. The integration of nanotechnology and advancements in computational methods promise further innovations, potentially transforming flexible hydrogel films into multi-functional materials with enhanced performance across diverse industries. As the technology matures, innovations in flexible hydrogel films are poised to redefine capabilities in personalized medicine, smart materials, and environmental sustainability, ensuring their continued relevance in the evolving landscape of materials science and engineering.
History
The development of hydrogel technology has a rich history, stemming from early research in polymer science. Hydrogels, defined as water-insoluble three-dimensional polymer networks capable of absorbing body fluids, have evolved significantly since their inception. Initially, simple hydrogels were created through basic physical crosslinking methods, but advancements have allowed for more complex structures utilizing chemical crosslinking mechanisms such as optical polymerization and enzymatic reactions
. In the 1960s, significant breakthroughs in synthetic hydrogels began to emerge, leading to their application in various medical fields, including tissue engineering and wound care. The biocompatibility and soft structure of hydrogels made them ideal for medical applications, as they mimic the extracellular matrix (ECM) of tissues, facilitating biological interactions. Over the years, research expanded to include diverse types of hydrogels, such as responsive hydrogels that react to environmental stimuli like temperature and pH, enhancing their utility in flexible electronics and sensors. This adaptability paved the way for innovative applications in energy storage, touch panels, and various sensor technologies. As synthetic strategies advanced, the production of conductive hydrogels became a focal point, marrying the fields of electronics and materials science. The emergence of smart materials and nanotechnology has further propelled the growth of hydrogel applications, allowing for the creation of multifunctional devices that integrate hydrogels with electronic components. This synergy continues to shape the future of flexible electronics, as researchers explore new methods of synthesis and functionality to address the growing demand for portable and efficient electronic devices.
Material Composition
Flexible hydrogel films are primarily composed of polymers, which are large molecules made up of repeated structural units called mers. These polymers are often derived from carbon-based materials combined with other elements like hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen, forming a diverse array of chemical structures that provide unique properties suited for various applications
. The selection of materials is critical in determining the performance characteristics of the hydrogel films, as the mechanical and physical properties of the base materials influence the final product’s functionality.
Types of Polymers in Hydrogel Films
Hydrogel films typically utilize three main types of polymers: thermoplastic polymers, thermosetting polymers, and elastomers. Thermoplastic polymers are notable for their ability to be reheated and reshaped multiple times without significant alteration of their molecular structure, making them highly versatile in manufacturing processes
. Examples include polyethylene and polystyrene, which can be utilized in different hydrogel formulations.
Structural Polymers
In addition to standard thermoplastics, structural polymers play a vital role in enhancing the mechanical properties of hydrogel films. These polymers may include additives such as stabilizers and plasticizers, which further enhance their functionality
. The incorporation of structural polymers into hydrogel films has led to advancements in applications such as flexible electronics, medical devices, and environmental sensors.
Composites and Blends
Hydrogel films may also integrate composite materials, where fixed shapes like fibers or particles are dispersed within the polymer matrix. This approach allows for improved strength and durability while maintaining flexibility
. The combination of different polymers can lead to blends that offer enhanced performance characteristics, catering to specialized applications in various industries.
Biodegradable and Sustainable Options
There is growing interest in the development of biodegradable polymers for hydrogel films, which aim to address environmental concerns associated with conventional polymer use. These materials present a challenge, as they tend to be more expensive and may not match the performance of traditional polymers
. However, innovations in polymer chemistry and design are paving the way for more sustainable alternatives in hydrogel technology.
Manufacturing Techniques
Overview of 3D Printing in Hydrogel Film Production
In the realm of flexible hydrogel film technology, 3D printing has emerged as a pivotal manufacturing technique, allowing for customized and complex geometrical designs that were previously unattainable. Initially, the focus was predominantly on the Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) method, but the landscape has since expanded to include other techniques such as Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), Stereolithography (SLA), and Semi-solid extrusion (SSE), each contributing uniquely to pharmaceutical applications and beyond
.
Advances in Rapid Manufacturing
The integration of 3D printing into rapid manufacturing processes has been recognized as a “next level” technology, especially for the production of flexible hydrogel films. These advancements enable the efficient creation of small batches of intricate parts, making it feasible to produce devices with tailored properties quickly and at lower costs
. Notably, the adoption of SLS and Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) shows promise in advancing rapid manufacturing capabilities within this domain.
Materials Utilized
The selection of materials plays a critical role in the manufacturing of hydrogel films. Traditionally, materials are categorized into metals, ceramics, or polymers, each presenting unique mechanical and physical properties that influence the choice of manufacturing techniques
. The development of specialized hydrogels has facilitated the adaptation of 3D printing, enabling innovations such as soft sensors and actuators that incorporate custom geometrical and functional features, significantly enhancing product customization and performance.
Applications in Healthcare
3D printing’s application in the healthcare sector demonstrates its impact on manufacturing techniques for hydrogel films. For example, the creation of patient-matched devices, such as bioresorbable tracheal splints for newborns, showcases the potential for individualized healthcare solutions
. Furthermore, the production of custom-fitted printed casts illustrates how 3D printing can enhance user comfort and facilitate recovery.
Future Directions
Looking ahead, the exploration of additive manufacturing in flexible hydrogel film technology holds significant promise. Researchers are investigating the possibility of utilizing 3D bioprinting to create complex tissue architectures, which could revolutionize regenerative medicine and other fields
. As the technology matures and becomes more accessible, its integration into various manufacturing processes is expected to expand, paving the way for innovative applications in both industrial and domestic settings.

Properties and Characteristics
Flexible hydrogel films exhibit a range of unique and valuable properties, primarily derived from their molecular composition and the specific processing techniques used during their production. The structural characteristics of these polymers, including their long chain molecular structure, branching, and cross-linking, significantly influence their final properties. Additionally, the processing methods, which may include flow orientation and other techniques, are crucial in determining the functionality and effectiveness of the hydrogel films in various applications
.
Barrier Properties
One of the defining features of hydrogel films is their barrier capabilities. While traditional materials like metals and glass provide nearly perfect barriers, hydrogels offer unique permeability characteristics that can be finely tuned. For instance, certain polar polymer structures within hydrogels can act as effective barriers to gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide. However, achieving these properties can complicate the melting and processing stages, as these same polar interactions hinder the ability to modify the material under heat without causing degradation
.
Mechanical and Environmental Resistance
Hydrogel films also demonstrate a remarkable balance between flexibility and strength, allowing them to maintain structural integrity in various environments. This is particularly important in applications that require durability against mechanical stress and environmental factors. The mechanical properties of hydrogels are influenced by factors such as molecular weight, cross-linking density, and the choice of monomers, which can be manipulated to achieve desired performance criteria
.
Synthesis and Innovation
The synthesis of flexible hydrogel films continues to evolve, opening opportunities for new systems with tailored permeability for diverse applications such as food packaging, biomedical devices, and agricultural products. Innovations in polymer chemistry are leading to the development of new materials that can better meet the demands of modern technology, particularly in terms of controlled permeability and resistance to environmental degradation
.
Applications
Innovations in flexible hydrogel film technology have garnered significant attention across various fields due to their unique properties and versatility. Hydrogel films are extensively used in tissue engineering, where they serve as scaffolds to improve or replace biological organs. Their structure closely resembles the extracellular matrix of tissues, enabling optimal cellular interactions and growth
.
Medical Applications
One prominent application of hydrogel films is in the creation of tissue-engineered constructs for regenerative medicine. These hydrogels can be designed to encapsulate cells and deliver drugs while maintaining their bioactivity, thus providing a sustained and tunable release of therapeutic agents at targeted sites
. For example, hydrogels are being used to create artificial skin and bone, where scaffold design must vary according to the specific tissue properties required. Additionally, 3D bio-printing technology has been integrated with hydrogel applications, allowing for the fabrication of complex tissue architectures that include vascular systems. This method involves layering living cells onto a gel medium, resulting in three-dimensional structures suitable for reconstructive surgery. The use of bioresorbable hydrogels in creating customized medical devices, such as tracheal splints for newborns, highlights the potential of hydrogels in addressing unique patient needs.
Soft Robotics
Hydrogels also play a significant role in the development of soft robotics. Their inherent flexibility and ability to change shape in response to environmental stimuli make them ideal materials for soft actuators and sensors
. Recent advances in hydrogel technology have facilitated the design of robotic materials that can mimic biological functions, leading to applications in areas such as assistive devices and prosthetics.
Environmental and Consumer Applications
Beyond the medical field, flexible hydrogel films have found applications in consumer products and environmental monitoring. Their ability to absorb water and release it gradually makes them suitable for agriculture, where they can help retain soil moisture and enhance plant growth. In addition, hydrogel films can be utilized in smart packaging solutions, providing real-time monitoring of food freshness and quality
.
Recent Innovations
Advances in Hydrogel Technology
Recent innovations in flexible hydrogel film technology have led to significant advancements in various applications, particularly in medicine and electronics. These developments focus on enhancing the functionalities of hydrogels, making them increasingly applicable in targeted drug delivery, tissue engineering, and smart sensor systems.
Smart Hydrogels
The emergence of smart hydrogels has been particularly noteworthy. These materials respond dynamically to environmental stimuli such as temperature, pH, and electric fields, enabling controlled drug release and enhanced functionality. For instance, electro-sensitive hydrogels can selectively modulate permeability based on electrical stimulation, allowing for precise control in drug delivery applications and biomechanical devices
. Moreover, light-responsive hydrogels are being explored for their ability to adapt to varying light conditions, further broadening their potential applications in biosensing and drug delivery systems.
Integration of Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is playing a crucial role in enhancing the properties of hydrogels. Researchers are integrating nanoparticles into polymer-based hydrogel systems to improve drug stability, loading capacity, and controlled release profiles. This integration not only enhances the effectiveness of drug delivery systems but also allows for targeted delivery mechanisms, where nanoparticles can guide the hydrogels to specific tissues or cells
.
3D Printing and Customization
The adoption of 3D printing techniques has opened new possibilities for the fabrication of customized hydrogel-based structures. This technology allows for the precise control over the shape and architecture of hydrogel implants and scaffolds, making it feasible to create patient-specific solutions for drug delivery and tissue regeneration
. Such advancements in additive manufacturing enhance the applicability of hydrogels in personalized medicine.
Multi-Functional Applications
Recent studies also emphasize the development of multifunctional hydrogels capable of delivering multiple therapeutic agents simultaneously. By enabling combination therapy within a single hydrogel matrix, these innovations aim to enhance therapeutic efficacy while minimizing side effects, thus addressing challenges such as drug resistance in various treatments
.
Challenges and Limitations
The development and application of flexible hydrogel films face several significant challenges and limitations. One major concern is property anisotropy, which can affect the mechanical performance of the films. Variations in the molecular structure and orientation within the hydrogel can lead to discrepancies in physical properties, making it difficult to predict behavior under different conditions
. Another critical limitation lies in the sensitivity of adhesive bonding to surface conditions. While advancements have been made in cleaning and treating surfaces to enhance adhesive performance, a better understanding of surface preparation is still needed to ensure reliable adhesion in practical applications. The lack of nondestructive quality control methods further complicates the widespread adoption of hydrogel films in industrial settings. Additionally, the high cost associated with advanced hydrogel materials presents a barrier to their use. The economic feasibility of producing large quantities of these materials must be addressed to facilitate broader market acceptance and application. Moreover, the complexity involved in the processing techniques required for these hydrogels, such as the precise control of spinning and the morphological characteristics of the fibers, adds to the challenge of achieving consistent quality and performance. Lastly, the emerging field of smart and intelligent materials, which includes hydrogel films, requires ongoing research and development to overcome these limitations. Future studies should focus on the synthesis, characterization, processing, and testing of hydrogel systems to improve their durability, processability, and economic viability. As the field advances, addressing these challenges will be critical to unlocking the full potential of hydrogel technologies.
Future Trends
Emerging technologies in flexible hydrogel film technology are poised for significant advancements, driven by a growing understanding of polymer properties and their applications. Researchers aim to predict intrinsic polymer characteristics, such as processing and end-use performance behavior, through advanced computational methods.
This predictive capability can enhance formulation processes and optimize conditions for developing new grades of existing products. As the focus shifts toward thermoset materials, particularly in high-performance applications like aerospace, innovations are anticipated in matrix resins and structural adhesives. The existing database for these materials is more developed than that for high-performance thermoplastics, indicating an area ripe for research and development. Enhancements in toughness and processing techniques for thermosetting systems and high-performance thermoplastics are critical needs that could shape the future landscape of hydrogel applications. Sustainability and environmental considerations are expected to play a crucial role in the future of flexible hydrogels. The rising demand for nonpolluting coatings and the push for reduced volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can lead to novel polymer systems and formulations that prioritize eco-friendliness. As regulatory pressures increase, the shift toward aqueous polymer systems and other sustainable approaches will likely gain momentum. The interconnected ecosystem of emerging technologies, including artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and advanced materials science, is anticipated to catalyze further innovations in flexible hydrogel films. This convergence will not only enhance the material properties of hydrogels but also broaden their applications in various fields, such as medical devices, sensors, and smart materials. Future trends will likely emphasize human-machine collaboration, enabling new methods of production and application that capitalize on the unique properties of flexible hydrogels.
Comments

Achieving a Perfect Fit: Tips for Using Your Screen Protector Cutter
“Achieving a Perfect Fit: Tips for Using Your Screen Protector Cutter” is a comprehensive guide designed to help users understand the nuances and best practices involved in using screen protector cutting machines.

Cadillac XT5 Navigation GPS Tempered Glass
Our XT5 Navigation Screen Protector offers superior protection for your GPS display. Featuring an oleophobic coatingfor optimal visibility.

Tips For How to Get Bubbles Out of Screen Protector
Are you frustrated by those pesky air bubbles ruining the look of your newly applied screen protector? You’re not alone. Many smartphone users struggle with getting air bubbles out of a screen after applying a new screen protector. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore effective methods to remove air bubbles from your screen protector, ensuring a smooth, clear display for your device. Whether you’re dealing with a glass screen protector or a plastic one, we’ve got you covered with expert tips and tricks.

EPU Matte Hydrogel Film For Cutter
Choosing a screen protector? This guide breaks down Matte EPU vs Glossy TPU, comparing their pros and cons to help you decide.

DIY Your Own Screen Protectors- The Magic of a Cutting Machine
“DIY Your Own Screen Protectors – The Magic of a Cutting Machine” explores the burgeoning trend of crafting custom screen protectors using advanced cutting machines.
Tags
Find All knowledge and trends from our blog, get the wholesale price and best quality from our factory.

What Film Cutting Machine and Its Application
Film cutting machines have played a crucial role in the evolution of filmmaking and various industrial processes by enabling precise cutting and splicing of film materials.

What Is a Screen Protector Cutting Machine?
A screen protector cutting machine is a specialized device designed to produce custom-fit screen protectors for various electronic devices, including smartphones, tablets, smartwatches, laptops, and monitors.
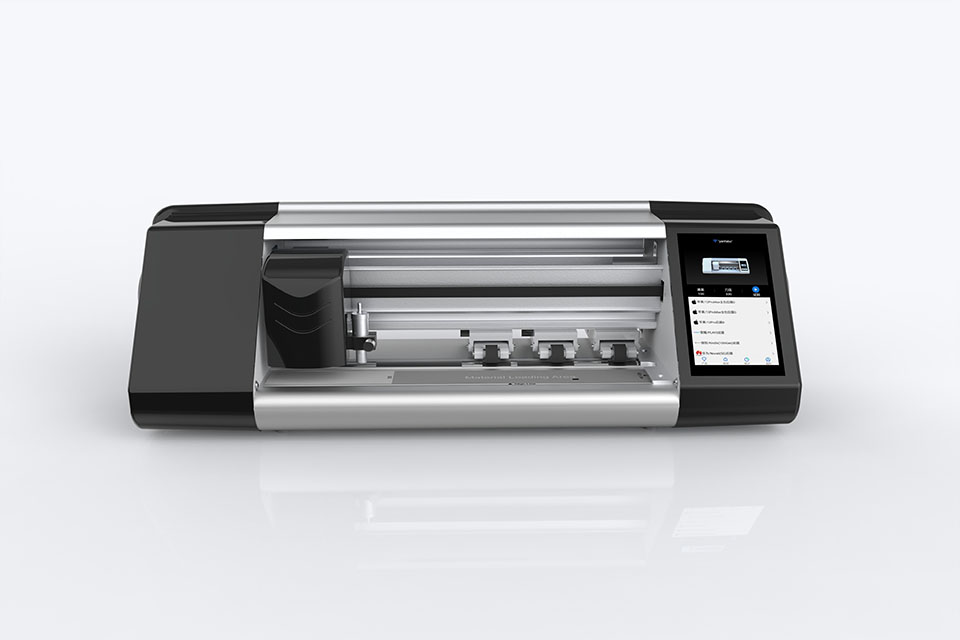

How Mobile Phone Screen Protector Cutting Machine Work?
A mobile phone screen protector cutting machine is a sophisticated device designed
to produce customized screen protectors for various digital devices with high preci
sion and efficiency.
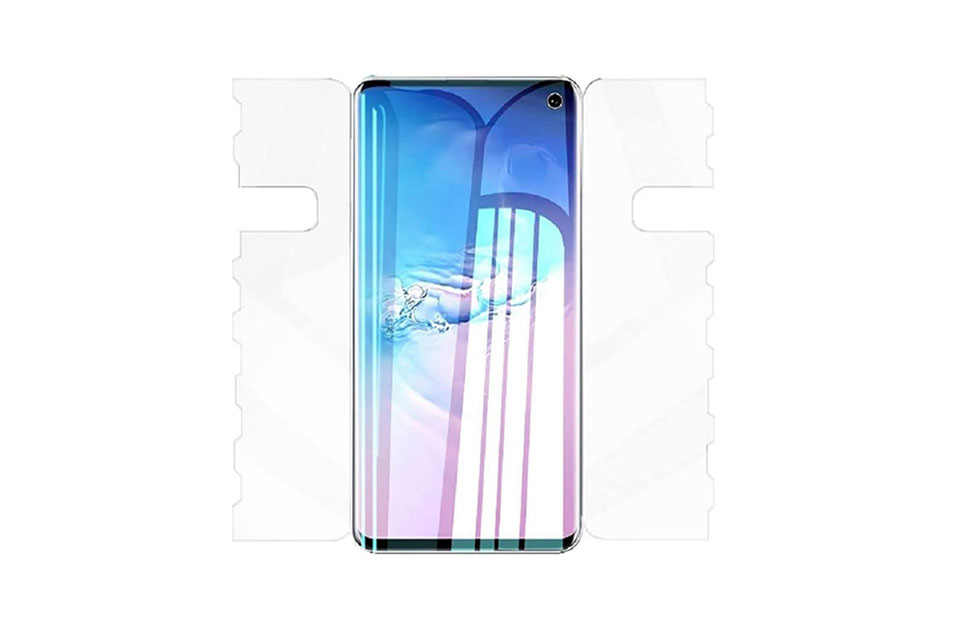

Characteristics of Mobile Phone Tempered Glass and Mobile Phone TPU Screen Protector
Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) screen protectors are flexible, durable, and
self-healing plastic films designed to protect electronic device screens from
scratches, impacts, and other potential damages.
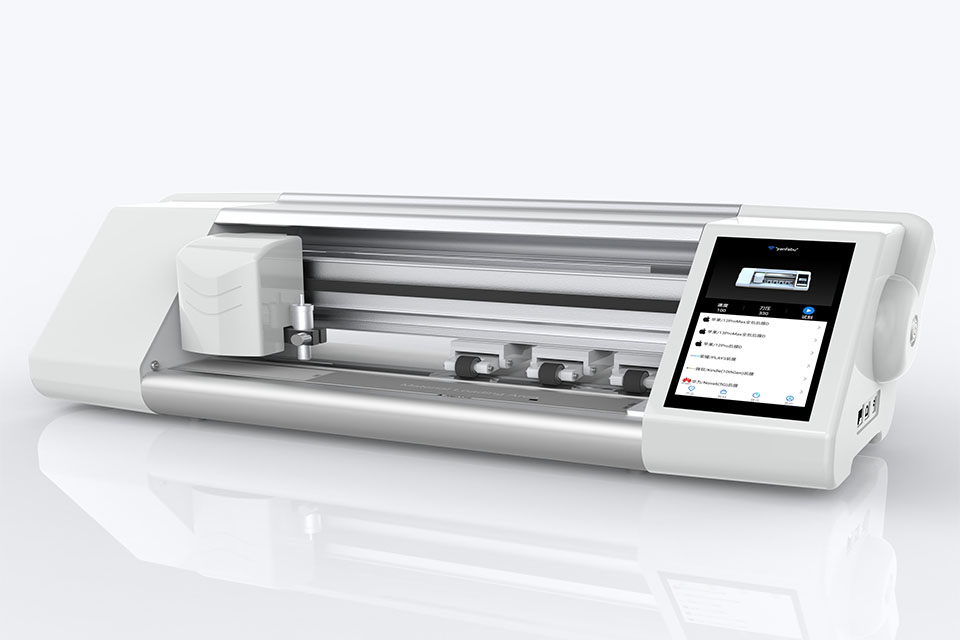

Revolutionize Device Protection with Screen Guard Cutting Machine
Whether you possess a smartphone, tablet, or smartwatch, this versatile machine accommodates a vast array of devices. It seamlessly adapts to the dimensions of your gadget, offering a custom fit that generic protectors can’t match.

Screen Protector Lifetime Warranty
A screen protector lifetime warranty is a guarantee provided by manufacturers that
promises to repair or replace a screen protector for the lifetime of the product, under specific terms and conditions.