The Ultimate Guide to Screen Hydrogel Film-Everything You Need to Know
Table of Contents
Extract
Summary
Notable for their superior impact absorption, self-healing capabilities, and high visual clarity, hydrogel films are increasingly favored by consumers seeking enhanced durability and usability for their devices. Their flexibility and ability to conform to various shapes make them particularly well-suited for both conventional and flexible electronic devices. Originating from advances in polymer science, hydrogels are three-dimensional polymeric networks capable of retaining significant amounts of water within their structures, giving them unique mechanical properties such as rubber elasticity and viscoelasticity. These properties are leveraged in the manufacturing of screen protectors, offering benefits such as superior impact resistance, bubble-free installation, and the ability to repair minor scratches over time. Despite these advantages, hydrogel protectors also face limitations, such as susceptibility to fingerprints and a potential lack of protection against severe impacts. The manufacturing process of hydrogel films involves several steps, including sample preparation, texture analysis, and methods like photopolymerization and chemical cross-linking, to ensure optimal mechanical properties. This detailed production process is crucial for creating high-quality hydrogel protectors that meet the rigorous demands of modern electronic devices. In addition to their application in mobile devices, hydrogel films have been employed across various industries, including medical, pharmaceutical, and food sectors, due to their versatile and adaptable properties. As the market for hydrogel films expands, so too does the focus on environmental impact and sustainability. Compared to traditional tempered glass protectors, hydrogel films require fewer resources and generate less waste, aligning with the increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly products. Furthermore, ongoing research and technological advancements promise exciting future trends, such as enhanced environmental responsiveness, advanced fabrication techniques, and improved mechanical properties, which will likely broaden the applications and appeal of hydrogel screen protectors.
History
The principles behind motion pictures were established long before cinema’s official birth. In 1832, Joseph Plateau introduced the phenakistoscope, a spinning disc that created the illusion of a moving image
. This paved the way for devices like the zoetrope in 1834, which produced animated images from a rapid succession of drawings. However, it wasn’t until photographic technology advanced enough to reliably capture sequential images that true motion pictures could be realized. In 1878, inventor Eadweard Muybridge used a row of 12 cameras with tripwires to take photos of a galloping horse, proving that all four hooves leave the ground at certain points during a horse’s gait. This breakthrough laid the basis for capturing and projecting moving photographic images. In 1888, Louis Le Prince created a camera that used celluloid film and paper loops with electronic timing mechanisms to capture 16 frames per second. Eastman Kodak soon began mass producing this flexible and durable celluloid film, originally invented in the 1870s. With this crucial advancement, the technical foundations for recording and exhibiting moving images were now in place. The breakthrough that allowed the motion picture industry to blossom was the development of the first modern movie camera. Several innovators built upon these foundations to develop the first mechanisms for shooting and exhibiting motion pictures. Thomas Edison led the way in 1891 with his Kinetoscope, a device containing a strip of perforated film that ran between a light source and magnifying lens. It allowed a single person to view short films through a peephole. In 1892, French inventor Léon Bouly designed the Cinématographe camera, which could both record and project films for audiences. This concept was expanded into a commercial exhibition device by Auguste and Louis Lumière, who held the world’s first film screening in 1895 in Paris. Other pioneers like William Friese-Greene and Wordsworth Donisthorpe tinkered with various types of cameras and projectors during this fertile period of innovation. Commercial exploitation began with the first Kinetoscope parlor opening on 14 April 1894, soon followed by many others across the United States and in Europe. Edison never attempted to patent these instruments outside the US, since they relied so greatly on technologies that were well-known and often patented in other countries. This period saw film transition from a scientific curiosity into an industry and popular medium. As moviemaking became more sophisticated, engineers and inventors continued enhancing the tools needed to make bigger, better, and longer films. Many core technologies like cameras, editing equipment, and projection systems were still in their infancy. Experimentation was common as pioneers tried to expand the boundaries of film. One major focus was improving projection to allow for larger screens and longer running times. Thomas Armat’s Phantoscope in 1895 pioneered techniques like intermittent film movement and fire shutters for projecting films without melting them. The silent era of cinema, spanning the two decades between 1895 and 1915, saw rapid technological advancements that paralleled the establishment of the first movie studios and the rise of film stars. The most pivotal advancement was Technicolor’s three-strip color process. Its vibrant hues and improved color accuracy revolutionized production design and cinematography.

Composition and Structure
Hydrogels are three-dimensional polymeric networks capable of retaining large amounts of water within their structures. The polymers used for hydrogel preparation can be categorized into two main types: natural and synthetic polymers. Natural polymers include hyaluronic acid, chitosan, heparin, alginate, gelatin, and fibrin. These natural hydrogels are generally non-toxic and offer benefits such as biocompatibility, biodegradability, and the ability to improve tissue regeneration, although their stability and mechanical strength are often lower than synthetic hydrogels
. Common synthetic polymers used in hydrogel preparation include polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol, sodium polyacrylate, and various acrylate polymers and copolymers. Hydrogels exhibit two primary regimes of mechanical properties: rubber elasticity and viscoelasticity. In the unswollen state, hydrogels can be modeled as highly crosslinked chemical gels described by the shear modulus, the Boltzmann constant, temperature, and the number of polymer chains per unit volume. In their swollen state, the stress-strain behavior can be characterized through true stress and engineering stress calculations during uniaxial extension or compression tests. The viscoelastic properties of hydrogels are highly dependent on the mechanical forces applied and their time dependence. The elasticity originates from the solid polymer matrix, while viscosity is attributed to the polymer network mobility and the aqueous phase components. Various physical models like the Maxwell and Kelvin-Voigt models are used to describe the time-dependent creep and stress-relaxation behavior of hydrogels. Additionally, hydrogels’ mechanical properties can be fine-tuned through various methods. By altering their hydrophobic properties, surface grafting onto stronger supports, or incorporating superporous hydrogel composites, the strength or elasticity of hydrogels can be significantly modified. The inclusion of nanoparticles and microparticles has also been shown to affect the stiffness and gelation temperature of hydrogels used in biomedical applications. A novel approach demonstrated by Shi et al. is the macroscopic supramolecular assembly (MSA) of rigid hydrogels. This method integrates different materials into sophisticated devices by creating a flexible spacing coating containing host or guest moieties that form supramolecular recognition at the interface. The MSA concept offers a new avenue for fabricating multi-material and multi-functional hydrogel devices.
Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of hydrogel films involves several steps and methodologies to ensure their optimal mechanical properties and functionality. Manufacturers employ various assessment techniques to evaluate the potential effects of different parameters on these films, focusing particularly on their mechanical properties such as tensile strength, puncture resistance, and compression strength. These evaluations are often carried out using instruments like Texture Analysers
.
Sample Preparation and Texture Analysis
One of the primary challenges in manufacturing hydrogel films is conforming to standard testing methods like ASTM or ISO due to the difficulty in preparing edible film samples for certain applications
. However, using texture analysis, gels can be assessed by measuring their mechanical resistance to stress. For instance, in a simple gel strength measurement, a cylindrical probe, such as the one used with a TA.XTplus Texture Analyser, is lowered into the gel system at a fixed speed. The gel strength is determined by the peak force required to reach a chosen distance, usually before permanent deformation. By penetrating further into the gel, the rupture force and elasticity/brittleness of the gel can also be measured. Standard probes required for ISO, AOAC, and GMIA standards tests are also available for assessing gel bloom or rupture.
Chemical and Physical Cross-linking
The mechanical properties of hydrogels are highly dependent on the type and quantity of crosslinks formed during their production. Chemical cross-linking involves the introduction of molecules between polymer chains to produce a cross-linked network. Common cross-linkers include glutaraldehyde and epichlorohydrin
. On the other hand, physical cross-linking can be achieved through freeze-thaw cycles, which form microcrystals within the polymer structure. Examples of this type of gelation include freeze-thawed gels of polyvinyl alcohol and xanthan.
Photopolymerization
Photopolymerization is another notable method for hydrogel production, where light, typically ultraviolet (UV) irradiation, is used to initiate polymerization. Photoinitiators added to the precursor solution cleave upon photon absorption, forming free radicals that start a polymerization reaction to create crosslinks between polymer strands. This reaction stops if the light source is removed, allowing for precise control over the amount of crosslinks formed. This technique is especially useful in cell and tissue engineering applications, as it enables the injection or molding of a precursor solution loaded with cells into a wound site, which can then be solidified in situ
.
Industrial Applications
The manufacturing of hydrogel films finds applications in various industries, including food, pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and cosmetics. For example, the development of gel capsules, contact lenses, and edible preserves benefits from assessing gel strength, elasticity, and rupture force. Additionally, hydrogel films are employed in wound dressings, jelly lubricants, and bacterial growth media due to their gel-forming properties. In products like toothpaste, creams, and pastilles, the strength of gels is utilized to modify the consistency of the end product
.
Applications
Hydrogel screen protectors have become increasingly popular due to their unique properties and wide range of applications. These protectors offer superior protection and an enhanced user experience compared to traditional tempered glass options.
Mobile Devices
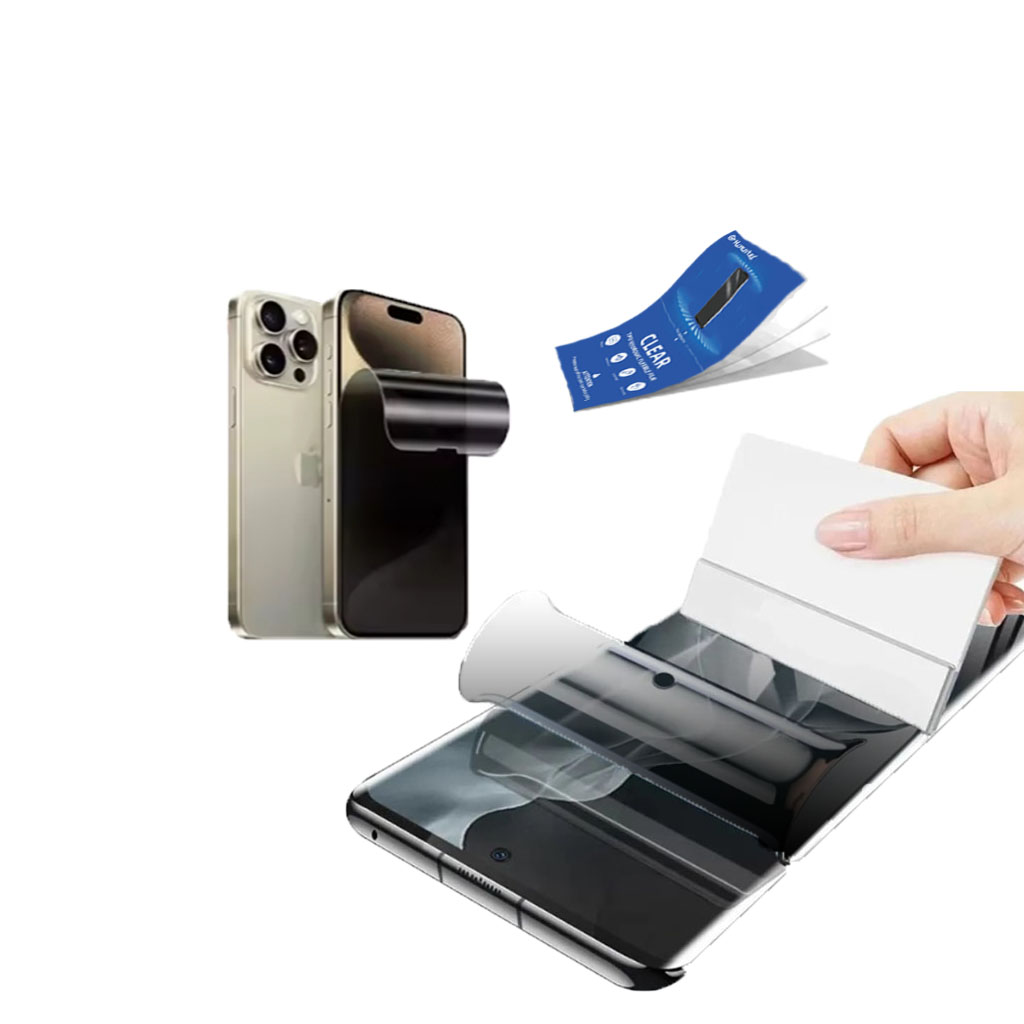
Hydrogel screen protectors are widely used to safeguard the screens of smartphones and tablets. Their excellent impact resistance ensures that the screens remain intact even when the device is dropped or subjected to significant force
. Additionally, the protectors are highly durable and long-lasting, making them a valuable investment for individuals who prioritize screen protection. Mobile phones, whether costing 200 or 800 euros, benefit from the added layer of security that hydrogel protectors provide, helping to keep devices operational and aesthetically pleasing.
Enhanced Usability
One of the most notable advantages of hydrogel screen protectors is their ability to enhance usability. Unlike traditional tempered glass, hydrogel protectors are resistant to fingerprints and smudges, making them easier to clean and maintain
. The installation process is also hassle-free, with no bubbles or residue left behind, allowing for a smooth, pristine look.
Flexible Devices
With the advent of flexible electronics, hydrogel protectors have found applications in protecting flexible devices as well. Their ability to conform to various shapes and maintain their protective qualities makes them ideal for use with devices that require flexibility
.
Cut-to-Size Applications
Hydrogel screen protectors can be cut to size, making them incredibly versatile. This innovation allows users to achieve a perfect fit for any device, eliminating the frustration of trying to align pre-cut protectors. This feature has revolutionized screen protection, making it more accessible and user-friendly
.
Comprehensive Device Protection
Companies like RizkaCreations.com offer intelligent TPU Hydrogel protective films that provide both front and back protection for over 3000 mobile phone models, including popular brands like Apple, Samsung, and Huawei
. This comprehensive approach ensures that not just the screen but the entire device is shielded from potential damage. By choosing hydrogel screen protectors, users can enjoy enhanced device longevity, improved usability, and peace of mind knowing that their screens are well-protected.
Key Properties
Hydrogel screen protectors are emerging as a versatile solution for protecting electronic device screens. Their key properties include superior impact absorption, self-healing capabilities, and high visual clarity, which contribute to their growing popularity among users.
Superior Impact Absorption
One of the main benefits of hydrogel is its ability to absorb impacts effectively. When a device with a hydrogel protector is dropped, the energy from the fall is distributed throughout the protector, significantly reducing the risk of screen damage. This property makes hydrogel protectors particularly useful for safeguarding delicate screens in everyday use and accidental drops
.
Self-Healing Capabilities
Hydrogel protectors possess self-healing properties, which allow them to repair minor scratches and marks over time. This feature ensures that the screen protector maintains a smooth and clear surface, keeping the device looking new for longer periods
. The self-healing mechanism involves the re-establishment of damaged bonds or structures within the hydrogel material, often through reversible bonds such as hydrogen bonding and host-guest interactions .

High Visual Clarity
Hydrogel screen protectors are designed to offer maximum visual clarity, ensuring that the quality of the phone’s display remains uncompromised. They maintain the crystal-clear clarity of the screen and do not interfere with touch sensitivity, providing an unaltered user experience
. This high level of transparency makes hydrogel protectors an attractive option for users who prioritize screen visibility and touch performance.
Bubble-Free Installation
The flexibility of hydrogel materials facilitates bubble-free installation, a common challenge with more rigid screen protectors. This ease of application is due to the hydrogel’s adaptability, which allows it to conform to the screen’s surface without trapping air bubbles underneath
.
Limitations
Despite their many benefits, hydrogel protectors are not without limitations. They are primarily effective against minor scratches and everyday wear and tear but may not provide adequate protection against severe impacts or deep scratches. Additionally, hydrogel protectors can attract fingerprints and smudges, necessitating regular cleaning to maintain their clear appearance
.
Installation and Usage
Installing a screen hydrogel film can be a meticulous process, but with the right steps and preparation, it can be done efficiently.
The Dry Installation Method
The dry installation method involves applying the screen protector directly onto your device’s screen without using any liquid. This method requires precision to ensure a bubble-free application.
- Clean the Device’s Screen: Use a microfiber cloth to remove any dirt, smudges, or fingerprints from the screen.
- Align the Screen Protector: Peel off the backing of the screen protector and carefully align it with the edges of your device’s screen.
- Apply the Screen Protector: Use a plastic card to gently press the screen protector onto the device’s screen, starting from the center and moving towards the edges to squeeze out any air bubbles.
- Finalize the Installation: Once you are satisfied that there are no air bubbles, your screen protector is successfully applied, and you can start using your device.
The Hinge Installation Method
The hinge installation method is similar to the dry installation method but adds a step to help accurately position the screen protector before adhering it to the screen.
- Clean the Device’s Screen: Use a microfiber cloth to remove any dirt, smudges, or fingerprints.
- Align and Secure the Screen Protector: Peel off the backing of the screen protector and place it carefully over the screen’s surface, aligning it with the edges of your device. Place narrow strips of tape along the top of the screen protector to hinge it in place.
- Fold and Apply the Screen Protector: Fold the screen protector back along the hinge to expose the device’s screen. Use a plastic card to apply the screen protector, starting in the middle and pressing outward.
- Remove Tape and Smooth Out Bubbles: Peel off the tape and smooth out any air bubbles by applying uniform pressure.
The Wet Installation Method
The wet installation method involves using a liquid adhesive to apply the screen protector, allowing for better adjustment during the application process.
- Prepare the Screen and Work Area: Clean the phone display thoroughly and ensure the work area is dust-free. Many protectors come with special wipes and stickers to pick off any leftover dust particles. Use a bright light to check the display from different angles.
- Apply Liquid Adhesive: Depending on the brand, you may need to spray a solution on the display or the protector. Carefully align the screen protector on your device’s screen.
- Adjust and Apply the Protector: Move the protector slightly until you are happy with the fit. Use the provided squeegee to remove any bubbles and excess liquid between the display and the protector. A final wipe on the top should leave you with a clean look.
- Drying Time: Leave the screen protector to dry for a few hours before using your device. By following these methods, you can ensure that your screen hydrogel film is applied smoothly and effectively, providing optimal protection for your device’s screen.
Market Analysis
The market for hydrogel films has seen a significant expansion across various industries, including food, medical, industrial, adhesive, and electronics sectors
. The increased demand for precise and reliable testing of gels has driven the standardization of gel testing methodologies, particularly with the use of texture analyzers like the TA.XTPlus Texture Analyzer family. This growth is fueled by the need to measure specific gel properties such as firmness, tackiness, relaxation, and swelling, which are critical for ensuring product quality and performance. Manufacturers in the automotive industry, for instance, utilize precise gels to encase potted electronics for car brakes, while the medical field employs silicone gels in prosthetics and bio-adhesive gels as drug delivery agents. The food industry also heavily relies on these texture analyzers to measure every type of food gel on the market. The necessity for rigorous testing is highlighted by customer feedback, emphasizing the potential financial implications of gel inconsistencies. One customer noted, “It was important to get twelve cents worth of gel right or we could incur thousands or millions of dollars in recall costs”. This underscores the critical nature of precise gel measurements in avoiding costly product recalls. Moreover, as the applications of gels and films continue to broaden, there is a rising need for assessing their mechanical properties through various techniques such as tensile, puncture, and compression methods, all of which can be conducted using texture analyzers. However, the transition from non-edible plastic packaging materials to edible films presents challenges in conforming to standard testing methods, thereby necessitating customized approaches to sample preparation and testing. The market’s dynamism is further reflected in the incorporation of advanced technology in testing equipment. For example, pharmaceutical companies have expanded their testing capacities by integrating temperature controls via Peltier testing plates into their TA.XTPlus Texture Analyzers, driven by the comprehensive support and training provided by manufacturers. As the market evolves, manufacturers must continue to innovate and adapt to the diverse and specific needs of various industries, ensuring that their products meet the stringent requirements of modern gel and film applications.
Environmental Impact
In an era of increasing environmental awareness, the sustainability of consumer products has become a top priority for many individuals. Hydrogel screen protectors present a more eco-friendly alternative compared to traditional tempered glass protectors. The production of tempered glass is highly energy-intensive and relies on non-renewable resources, whereas hydrogel requires fewer resources and generates less waste during its manufacturing process, making it a greener choice for environmentally conscious consumers
. Moreover, the longevity of hydrogel screen protectors significantly contributes to their reduced environmental footprint. Unlike tempered glass, which is prone to shattering upon impact and often needs frequent replacements, hydrogel protectors offer exceptional durability and longevity due to their resilient yet flexible composition. This means fewer replacements over time, further diminishing their overall environmental impact. Additionally, the self-healing properties of hydrogel play a crucial role in maintaining a flawless appearance and extending the product’s lifespan. By re-establishing damaged bonds or structures, hydrogel protectors can recover from daily wear and tear, thereby reducing the need for premature replacement. This capability aligns with the growing consumer demand for maintenance-free and long-lasting products, promoting a more sustainable approach to screen protection.
Future Trends
The future of screen hydrogel film technology promises exciting developments driven by ongoing research and technological advancements. Scientists and engineers are actively exploring new directions to enhance the properties and applications of hydrogels, pushing the boundaries of what these materials can achieve
.
Environmental Response
One significant area of focus is improving the environmental responsiveness of hydrogel films. Researchers are developing new formulations that can respond to various environmental stimuli, such as temperature, pH, and light, to optimize their performance in different conditions
. This capability is crucial for applications in smart coatings, sensors, and biomedical devices.
Advanced Fabrication Techniques
Emerging fabrication techniques, including 3D printing and nanotechnology, are set to revolutionize the production of hydrogel films. These advanced methods allow for more precise control over the film’s structure and properties, enabling the creation of highly customized hydrogel materials with enhanced functionality
.

Enhanced Mechanical Properties
Improving the mechanical properties of hydrogel films remains a critical goal. Innovations in cross-linking methods and the incorporation of novel materials are expected to yield hydrogels with superior strength, flexibility, and durability. These enhancements will expand the potential applications of hydrogels in fields such as soft robotics, flexible electronics, and wearable devices
.
Sustainable and Cost-Effective Solutions
As the demand for eco-friendly materials grows, there is a strong push towards developing sustainable hydrogel films. Researchers are exploring renewable resources and greener synthesis methods to reduce the environmental impact and energy costs associated with hydrogel production
. These efforts aim to make hydrogel technologies more accessible and commercially viable.
Biomedical Innovations
The medical field continues to be a major beneficiary of hydrogel research. Future trends include the development of hydrogels with improved biocompatibility and targeted drug delivery systems. These innovations hold promise for more effective treatments and therapies, particularly in wound care, tissue engineering, and regenerative medicine
.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration
The future of hydrogel technology will likely see increased collaboration between disciplines such as materials science, chemistry, biology, and engineering. This interdisciplinary approach is essential for overcoming existing challenges and unlocking new applications for hydrogel films. By leveraging the expertise of diverse fields, researchers can drive the innovation needed to propel hydrogel technology forward
.
Comparisons with Other Screen Protectors
When selecting a screen protector for your device, the choice often boils down to plastic, tempered glass, and liquid screen protectors, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Liquid Screen Protectors
Liquid screen protectors are an innovative alternative that involves applying a nano-liquid solution to the screen, forming an invisible protective layer once dried. They are extremely lightweight and add no bulk to the device, offering high transparency and smoothness
. However, liquid protectors are less effective against drops and severe impacts compared to tempered glass. They offer minimal protection from everyday scuffs but can leave the screen vulnerable to significant damage.
Plastic Screen Protectors
Plastic screen protectors, often made from polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), are known for their affordability and ease of installation. They offer basic protection against scratches and minor impacts but fall short when it comes to significant drops and high-impact resistance
.
Tempered Glass Screen Protectors
Tempered glass screen protectors are renowned for their strength and durability. They undergo a chemical or heat treatment process to enhance their hardness, making them up to four times stronger than non-tempered glass
. Tempered glass offers excellent protection against scratches, shocks, and direct impacts, providing a rigid and scratch-resistant layer that can withstand significant impacts. Furthermore, they provide high visual clarity and a smoother tactile feel, simulating the experience of using the device’s actual screen. While tempered glass protectors are pricier, they offer unparalleled protection against drops and are resistant to scratches from sharp objects like keys and knives. However, tempered glass can shatter under severe impacts, and its rigid nature means it does not conform to the screen’s shape over time.
Cost and Practicality
In terms of cost, liquid screen protectors generally come at a higher price point for a single application, but they can be used on multiple devices if there’s leftover liquid
. On the other hand, a combo pack of tempered glass screen protectors can be more economical, providing multiple protectors at a lower cost per unit.
User Reviews and Feedback
Reports from users who have opted for My Devia’s hydrogel screen protectors are largely positive. Many highlight the durability and self-healing capabilities as strong points, in addition to preserving the device’s original touch experience
. Users often emphasize the cost-benefit aspect, noting that while the initial investment may be greater, the long-term protection and self-healing properties can represent significant savings over time. One of the main advantages users appreciate is the screen protector’s ability to maintain the device’s original touch sensitivity. This ensures that the user experience remains unaffected, which is a crucial factor for many smartphone owners. Additionally, the self-healing qualities of hydrogel protectors are praised for effectively managing minor scratches and abrasions, enhancing the longevity of the device screen. However, some drawbacks have been reported. While hydrogel protectors excel at preventing small scratches and maintaining screen clarity, they are less effective at protecting the device from severe impacts or strong blows. Users have also noted that hydrogel protectors are more susceptible to fingerprints and smudges, requiring regular cleaning to maintain optimal visibility
Comments

Achieving Precision: Best Practices for a Snug Fit with Screen Protector Cutters
Achieving precision in cutting screen protectors is crucial for ensuring optimal device protection and user satisfaction.

Top 5 Budget-Friendly Screen Protector Cutting Machines for Small Businesses
In the rapidly evolving world of mobile accessories, providing custom-fit screen protectors for a wide range of devices has become essential for small businesses, and investing in the right screen protector cutting machine is crucial for success.
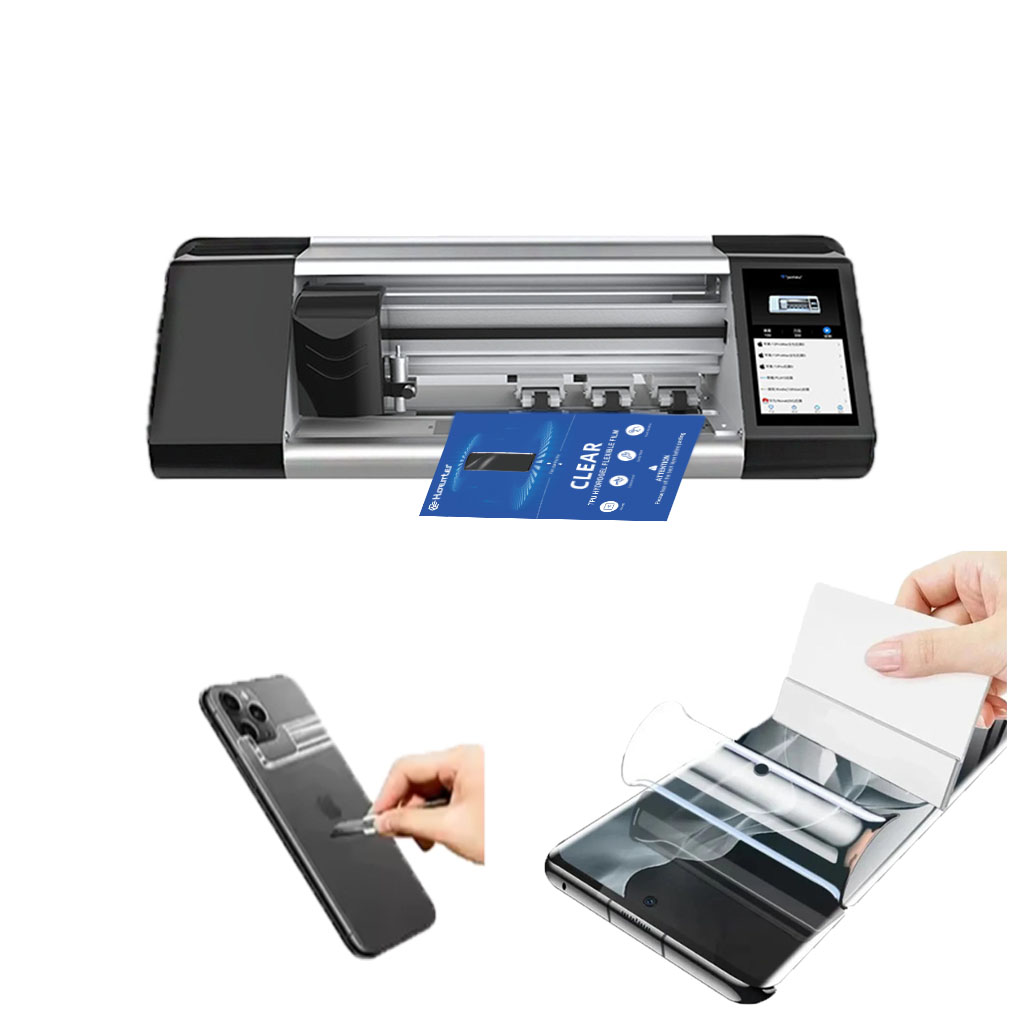

Hydrogel Screen Protector Cutting Machine
Hydrogel cutting machines excel at handling soft, flexible materials and are generally more cost-effective for simple designs.
Laser cutting machines offer superior precision, especially for complex cutouts, and greater material versatility.
The choice between hydrogel and laser cutting depends on factors like production volume, material types, and design complexity.
Consider long-term costs, including maintenance and energy consumption, when making your decision.
Both technologies continue to evolve, with future trends focusing on AI integration and eco-friendly solutions.

How to Clean Paperlike Screen Protector?
By following these tips, you can ensure that your Paperlike screen protector stays clean, functional, and enjoyable to use for years to come!

Where to Repair My Phone
With this guide, you’re equipped to make informed decisions about your phone repairs, ensuring your device remains a reliable companion in your daily life.
Tags
Find All knowledge and trends from our blog, get the wholesale price and best quality from our factory.
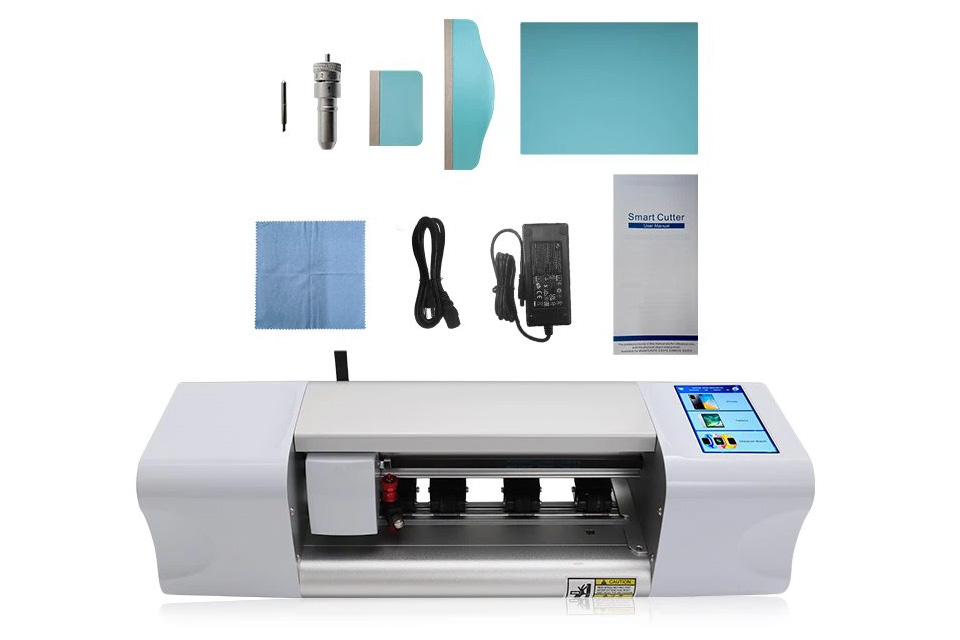

What Film Cutting Machine and Its Application
Film cutting machines have played a crucial role in the evolution of filmmaking and various industrial processes by enabling precise cutting and splicing of film materials.
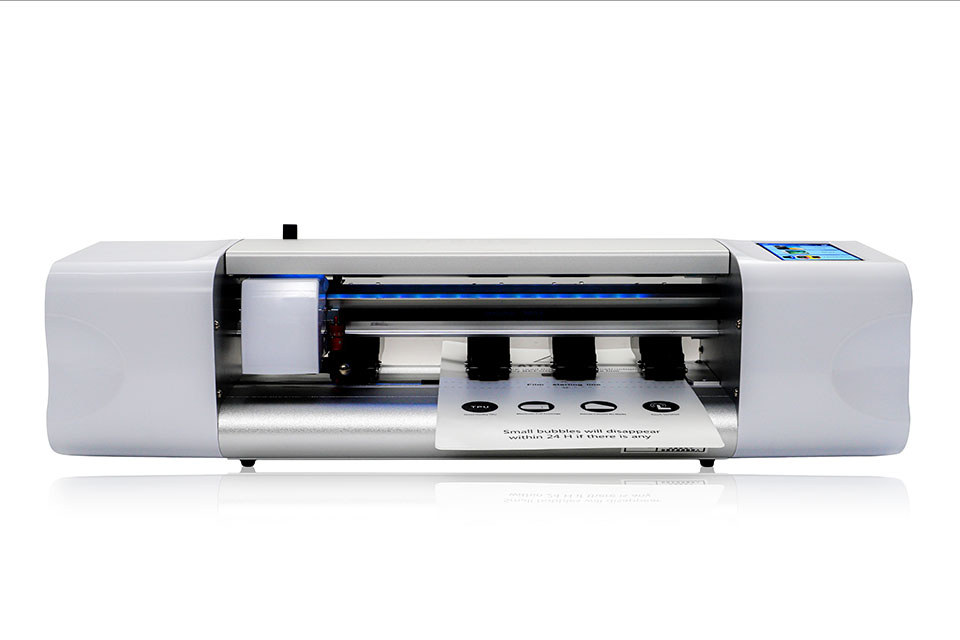

What Is a Screen Protector Cutting Machine?
A screen protector cutting machine is a specialized device designed to produce custom-fit screen protectors for various electronic devices, including smartphones, tablets, smartwatches, laptops, and monitors.
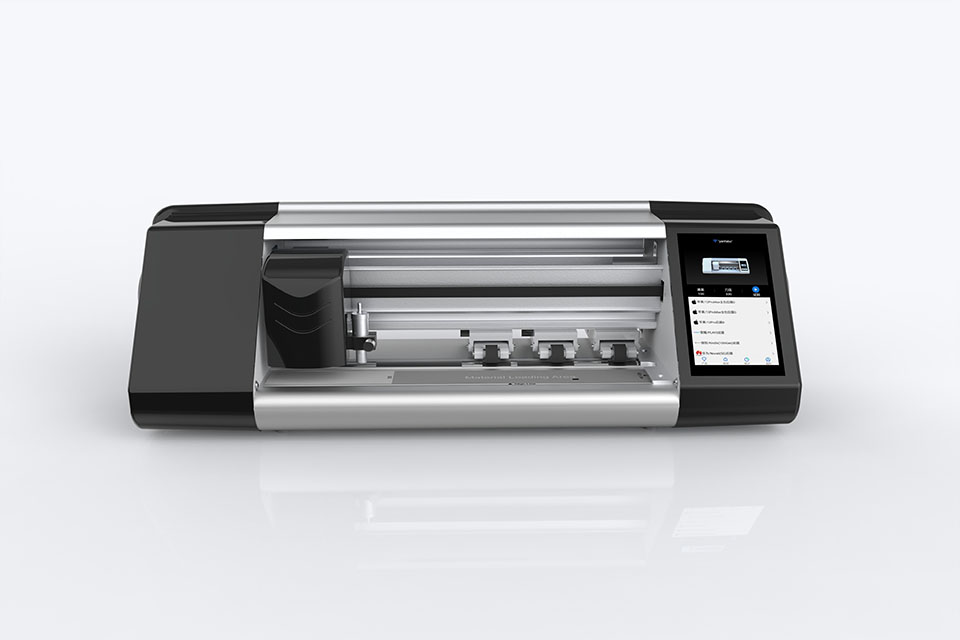

How Mobile Phone Screen Protector Cutting Machine Work?
A mobile phone screen protector cutting machine is a sophisticated device designed
to produce customized screen protectors for various digital devices with high preci
sion and efficiency.
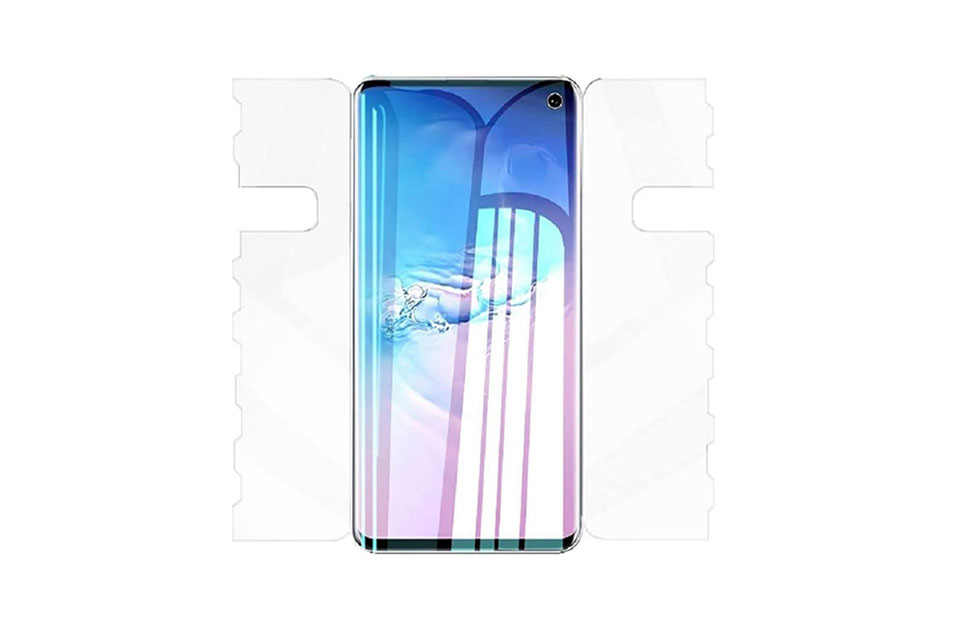

Characteristics of Mobile Phone Tempered Glass and Mobile Phone TPU Screen Protector
Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) screen protectors are flexible, durable, and
self-healing plastic films designed to protect electronic device screens from
scratches, impacts, and other potential damages.
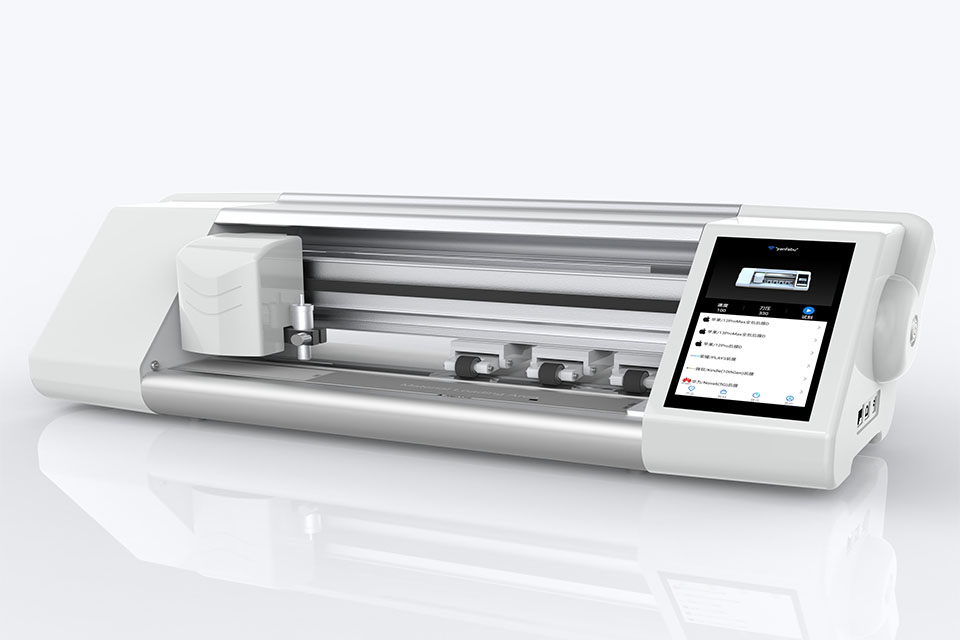

Revolutionize Device Protection with Screen Guard Cutting Machine
Whether you possess a smartphone, tablet, or smartwatch, this versatile machine accommodates a vast array of devices. It seamlessly adapts to the dimensions of your gadget, offering a custom fit that generic protectors can’t match.

Screen Protector Lifetime Warranty
A screen protector lifetime warranty is a guarantee provided by manufacturers that
promises to repair or replace a screen protector for the lifetime of the product, under specific terms and conditions.